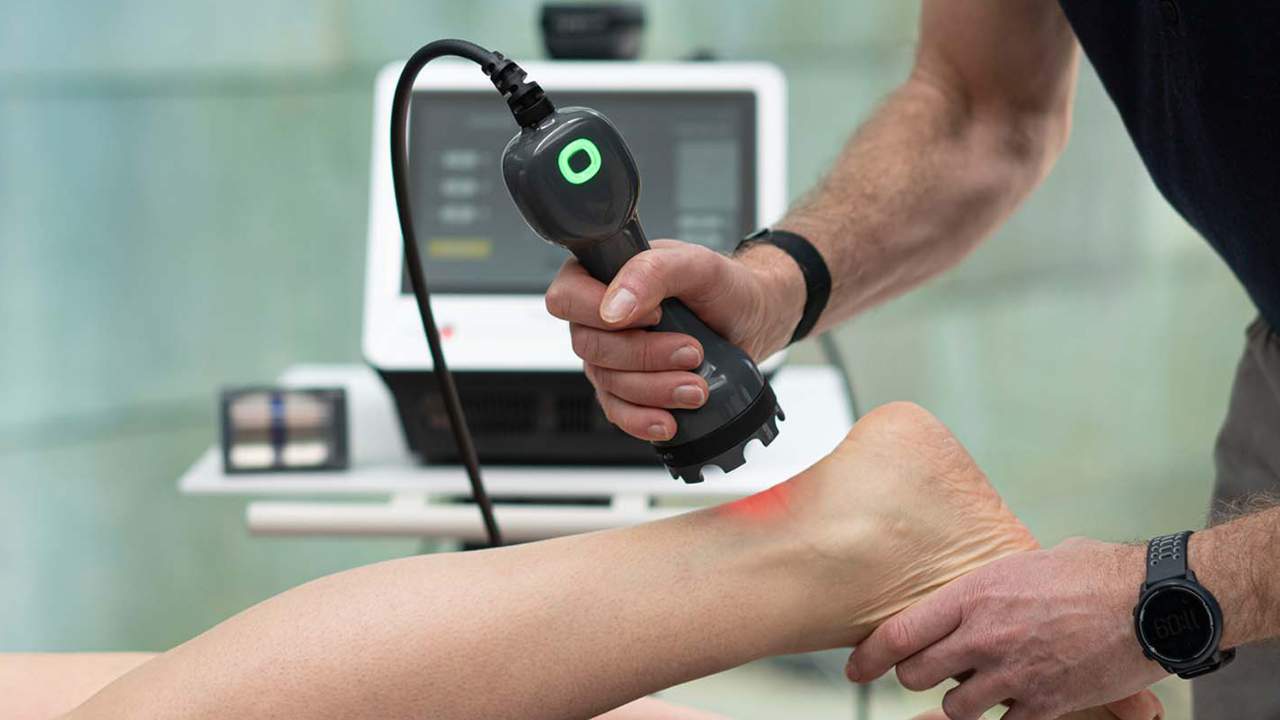
Laser therapy, a cutting-edge medical technique that uses the power of light for therapeutic reasons, has shown exceptional efficacy in a variety of healthcare settings. However, as with any medical treatment, it is critical to identify scenarios in which laser therapy may be contraindicated to maintain patient safety and avoid unwanted side effects.
Contraindications are specific conditions or circumstances in which the use of laser therapy is improper or dangerous to the user. Addressing these contraindications is critical for healthcare practitioners because it guides their decision-making process when recommending or providing laser therapy.
A thorough examination of a patient's medical history, current health status, and potential risk factors is required to determine whether laser therapy is the best course of action. To learn more here you can visit Domer’s official site. From pregnancy and cancer to illnesses affecting the eyes and skin, each contraindication is critical in personalizing treatment strategies to individual needs.
Contraindications for Laser Therapy
Laser therapy has gained popularity as a non-invasive and efficient treatment option for a variety of medical ailments. However, it is critical to understand that, like every medical intervention, laser therapy has its own set of contraindications - instances in which its use may be improper or potentially hazardous. Understanding these contraindications is critical for healthcare workers seeking to protect their patients' safety and well-being.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a major contraindication for laser therapy, particularly during the first trimester. While the hazards have not been demonstrated, the possible effect of laser therapy on fetal development warrants care. Healthcare practitioners frequently avoid using laser therapy on pregnant patients unless the benefits outweigh the hazards, and even then, a thorough risk-benefit analysis is required.
Cancer
Laser therapy is generally not recommended in the presence of cancer, especially if the treatment site is near a tumor or the patient has a history of cancer. The risk is that increased cellular activity and blood flow may accidentally promote cancer cell growth. Any use of laser therapy in cancer patients should be carefully considered and coordinated with the oncology team.
Eyes and Thyroid Gland
Direct exposure to laser light is a severe contraindication due to the risk of retinal damage. Protective eyewear is essential during laser therapy sessions to avoid eye harm. Furthermore, while using laser therapy on the thyroid gland, caution is advised because the effects on thyroid function are not fully understood, and there is a potential danger of aggravating thyroid disorders.
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
Patients with a history of epilepsy or seizure disorders are generally thought to be at a higher risk during laser therapy treatments. Some lasers' flickering or pulsating characteristics may cause seizures in sensitive people. As a result, healthcare practitioners must carefully weigh the risks and benefits before providing laser therapy to patients who have a history of seizures.
Photosensitivity
Photosensitive individuals, whether due to medication, medical conditions, or genetic predisposition, may experience unpleasant effects from laser therapy. Rashes, burns, and other skin abnormalities are examples of photosensitivity reactions. Patients taking photosensitizing medications, such as some antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), should notify their doctor before receiving laser therapy.
Impaired Sensation
Laser therapy uses patient input to ensure that the treatment intensity is suitable. Individuals with decreased sensibility, such as those with peripheral neuropathy, may not be able to detect heat or discomfort throughout the operation. This lack of input may result in overexposure and harmful effects.
Skin Conditions and Infections
Active skin infections or open wounds at the treatment location are contraindications to laser therapy. The increased blood flow and cellular activity caused by laser therapy may worsen infections or impede the natural healing process. Furthermore, individuals with a history of keloid formation or hypertrophic scarring should exercise caution because laser therapy has the potential to affect scar tissue formation.
Remarks
While laser therapy has numerous benefits for a variety of medical issues, understanding its contraindications is critical to maintaining patient safety and optimal treatment outcomes. Healthcare practitioners should conduct thorough assessments that take into account the patient's medical history as well as their current health status. Open communication between healthcare professionals and patients is vital for addressing concerns and tailoring treatment plans accordingly.